Seven Questions on Governor
Question.1. Draw a neat sketch of centrifugal governor.
Answer.
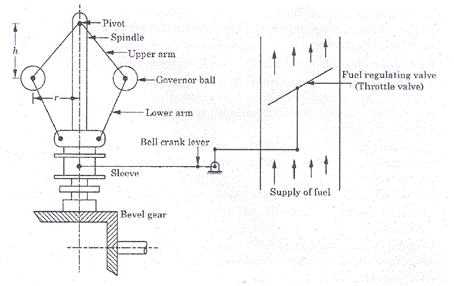
Fig. Centrifugal Governor
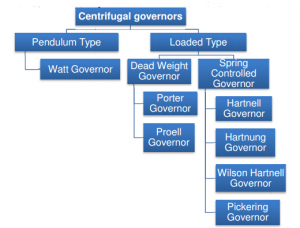
Question.2. Classify centrifugal governors.
Answer.
Question.3. Differentiate between flywheel and governor.
Answer.
|
Sr. no. |
Flywheel |
Governor |
|
1. |
The function of a flywheel is to control the fluctuation of speed due to variation in the engine turning moment during each cycle of motion. | The function of governor is to control the fluctuation of speed due to variation in the load over a period of time. |
|
2. |
It works continuously in each cycle. | It works intermittently when the load varies. |
|
3. |
A flywheel stores energy when it is available in excess of the load requirement and gives the same when it is less than the requirement. | A governor regulates the speed by controlling the quality or quantity of fuel according to the load requirements. |
|
4. |
A flywheel may not be used when there is no undesirable cyclic fluctuation of energy output | The governor is essential for all types of engines as it adjusts the supply according to demand. |
|
5. |
A flywheel does not have any control over the quality or quantity of the working fuel. | A governor has control over the quality and quantity of the working fuel. |
|
6. |
It is provided on engines and fabricating machines such as shear machines, punching machines etc. | It is provided on prime movers such as engines and turbines etc. |
Question.4. Derive an expression for the height of a porter governor.
Answer.
Porter governor is modification of a simple Watt governor. A central load is attached to the sleeve as shown in fig. The central load moves along the central spindle. This additional downward force increases the speed of rotation required to enable the balls to rise to any predetermined level.
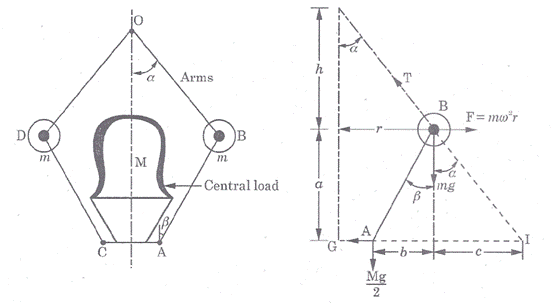
Fig. Porter Governor

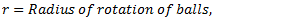
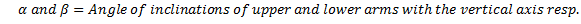
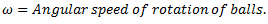
Neglecting the friction between the spindle and sleeve and considering the equilibrium of right half configuration, let us take moments about I.
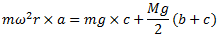
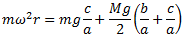
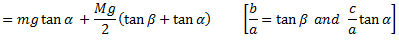
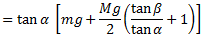
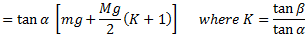
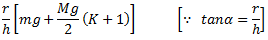
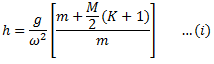
if the arms of the governor are equal and pivoted on the axis of spindle or are at equidistant from the axis of spindle, then
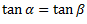
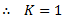
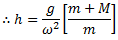
Now let us consider the force of friction between the sleeve and the spindle.
The force of friction always acts in a direction opposite to that of motion. Thus, when the sleeve move upward, the force of friction on sleeve acts downward. Similarly, when sleeve moves downward, the force of friction on sleeve acts upward. In general, the net force acting on the sleeve is 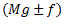 depending upon the movement of sleeve.
depending upon the movement of sleeve.
After considering friction, the equation (i) becomes
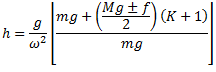
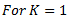
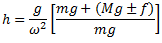
Question.5. Explain the construction and working of hartnell governor with the help of neat sketch.
Answer. Hartnell governor is a spring loaded governor. Initially, the spring is fitted in compression so that a force is applied to the sleeve. It consists of two bell crank levers hinged in the frame. The frame is attached to the governor spindle and therefore, rotates with it. Each bell crank lever carries a mass at one and a roller at the other. The rollers fit into a groove in the sleeve as shown in fig.
As the speed increases, the balls move away from the spindle axis, the bell crank levers move on the pivot and lift the sleeve against the spring force. As the speed decreases, the sleeve moves downwards. The movement of the sleeve is further taken to the throttle of the engine. The spring force can be adjusted with the help of a screw cap nut.
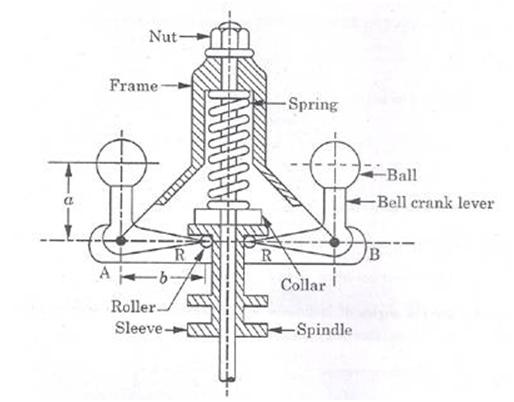
Fig. Hartnell Governor
Q.6. Derive an expression for the effort of a governor.
Answer.
When a governor is running at constant speed, it is in equilibrium and the net force acting on the sleeve is zero. If the load on the engine changes, the speed also changes and hence, the sleeve of the governor changes its position. This can take place only if, a certain force acts on the sleeve and the sleeve will occupy a new equilibrium position when the resultant force acting on it becomes zero again. The average force which acts on the sleeve for a given percentage change of speed is called effort of the governor.
The governor effort may be calculated in the following way:
Let us consider a Porter governor. Let 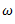 be the equilibrium speed of the governor and let it change to
be the equilibrium speed of the governor and let it change to 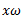 .
.
If the arms of the governor are equal and pivoted on the axis of rotation, then
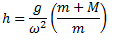
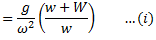
Let R is the force applied on the sleeve which prevents its motion at new speed 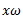 .
.
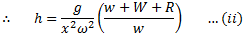
Dividing equation (i) by (ii), we get
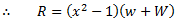
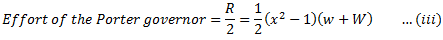
Let  is the frictional force between the sleeve and the spindle of the governor, then
is the frictional force between the sleeve and the spindle of the governor, then
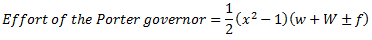
Let 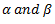 are the angles of inclination of the upper and lower arms with the axis of governor spindle respectively, then neglecting friction,
are the angles of inclination of the upper and lower arms with the axis of governor spindle respectively, then neglecting friction,
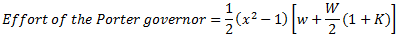
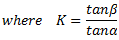
For a simple watt governor,
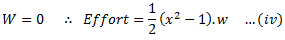
It can be seen from the equation (iii) and (iv) that the effort of Porter governor is more than Simple Watt governor.
Question.7. Derive an expression for the power of governor.
Answer.
Power of a Governor : The power of governor is defined as the workdone on the sleeve of governor for a given percentage of change in speed of the governor. It is calculated by the product of effort and the displacement of the sleeve.
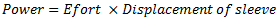
Let us consider a Porter governor. Let 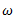 be the equilibrium speed of the governor and let it changes to
be the equilibrium speed of the governor and let it changes to 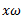 .
.
If the arms of the governor are equal and pivoted on the axis of rotation, then
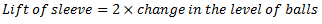
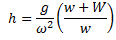
At new speed 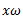 ,
,
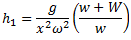
Change in the level of balls,
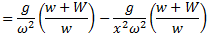
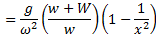
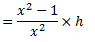
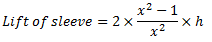
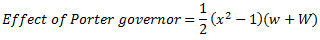
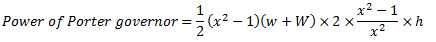
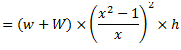
For a simple Watt governor,
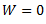
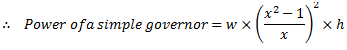
6 Responses to “Seven Questions on Governor”
Rupesh kumar
Good exercise material
saurabh rawat
Material is good but u should add some numerical portion also so that your material will be best!!
admin
You are right, I will try to update it as much as possible.
Thanks for the comment.
Ramnaresh
Porter governor form relativ quiesion given
Linght of arm-250mm and ball ka mass -10kg and central mass-20kg. Governor ki radi-150mmand200mm than governor ki maxiam speed and paras speed
kanahaiya kumar
Discuss the effect of friction on the functioning of a porter governor?
JITENDRA KUMAR
I have a question please,
Q. Why central weight applied on porter governor ?.