Introduction of Machine design:
The term design can be defined as the formulation of a plan for the satisfaction of human need.
Design means to create something new or arrange existing things in a new order to satisfy a recognized need of society.
Mechanical engineering design means the design of the parts, products and systems of mechanical nature. It deals with all the disciplined of mechanical engineering, such as machine design, thermal engineering, fluid power engineering, refrigeration and air conditioning etc.
Machine design deals with the design of machines, mechanisms and their elements. The design of machines or mechanisms ultimately comes to the design of their individual elements.
Machine design is the process of selection of the materials, shapes, sizes and arrangements of mechanical elements so that the resultant machine will perform the prescribed task.
Design of machine element can be defined as the selection of material and the values for independent geometrical parameters so that the element satisfies its functional requirements and undesirable effects and kept within the permissible limits.
The concept of machine design may be illustrated in the figure below.
Figure: Concept of Machine Design
For example, the process of design of a belt drive consists of:
- Selection of arrangement of mechanical elements like pulleys, belt, shaft, keys bearings etc.
- Selection of shapes of these elements.
- Selection of materials of these mechanical elements.
- Selection of sizes of these mechanical elements.
Most of the problems in mechanical engineering design or specifically in machine design, do not have a unique right answer. There are nearly endless number of workable designs, none of which could be called an incorrect answer. But of the correct answers, some are obviously better than others.
Design Procedure:
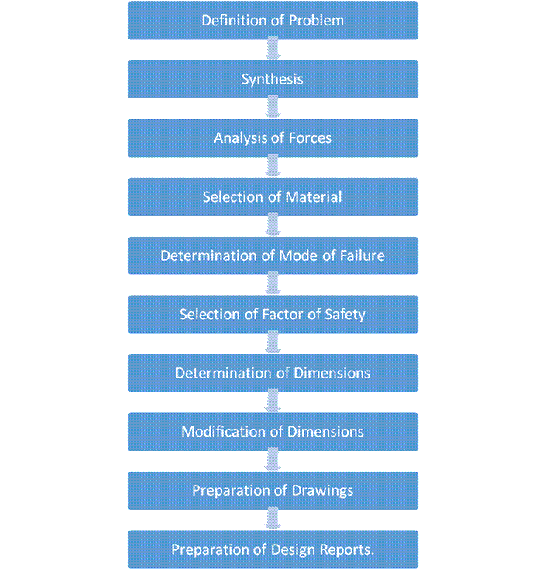
Figure: Design Procedure
The general procedure that is followed in machine design is given in the above figure. It consists of following steps:
1. Definition of Problem:
Define the design problem giving all input parameters, output parameters and constraints.
2. Synthesis:
Once the problem is defined, the next step is synthesis. Synthesis is the process of selecting or creating the mechanism for the machine and the shapes of the mechanical elements so as to get the desired output with the given input.
3. Analysis of Forces:
Draw the free body diagram of each element of the machines. Find out the forces (including moments and torque) acting on each element by force analysis.
4. Selection of Material:
Select the suitable material for each element. Four basic factors that are to be considered while selecting the materials are: availability, cost, mechanical properties, and manufacturing considerations.
5. Determination of Mode of Failure:
Before finding out the dimensions of the elements, it is necessary to know the type of failure by which the element will fail when put into the use.
6. Selection of Factor of Safety:
Based on the application, select the factor of safety. Knowing factor of safety and material strength, determine the permissible or design stress.
7. Determination of Dimensions:
Find the dimensions of each element of the machine by considering the forces acting on the element and the permissible stress.
8. Modification of Dimensions:
Modify the dimensions of the elements on the higher side, if required, based on the following considerations:
- Selection of standard parts available in the market.
- Convenience of assembly
- Convenience of Manufacturing.
9. Preparation of Drawings:
Prepare working drawing of each element or component with minimum two views showing following details:
- a. Dimensions
- b. Dimensional Tolerances
- c. Surface Finish
- d. Geometrical Tolerances
- e. Special production requirement like heat treatment
Prepare assembly drawing giving part number, overall dimensions and part list
The component drawing is supplied to the shop floor for manufacturing purpose, while assembly drawing is supplied to the assembly shop.
10. Preparation of Design Report
Prepare design report containing details about step 1 to step 8.
DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS:
Design considerations are the characteristics which influence the design of the element or perhaps, the entire system. Normally, a number of such characteristics have to be considered in any design problem.
In a given design problem, the design engineer should identify the various design considerations and incorporate them in the design process in their order of importance.
For example, in the design of a spring, two most significant design considerations are strength and stiffness.
Some of the common design considerations are as follows:
1. Strength
2. Rigidity
3. Reliability
4. Safety
5. Cost
6. Weight
7. Ergonomics
8. Aesthetics
9. Manufacturing
10. Conformance to Standards
11. Assembly
12. Friction and Wear
13. Life
14. Vibrations
15. Thermal considerations
16. Lubrication
17. Maintenance
18. Flexibility
19. Size and Shape
20. Stiffness
21. Corrosion
22. Noise
The various design considerations, listed above, are discussed as follows:
1. Strength
The machine elements are subjected to any one or combination of loads like forces, bending moments and torque
A machine element should have sufficient strength to avoid failure either due to yielding or due to fracture under the loads.
2. Rigidity
A machine element should have sufficient rigidity so that its linear as well as angular deflections, under the loading are within permissible limits.
3. Reliability
The reliability is defined as the probability that a component, system or device will perform without failure for a specific period of time under the specified operating conditions.
A machine element should have reasonable good reliability so that it can perform its function satisfactorily over its life span.
4. Safety
A machine element should be designed such that it ensures safety of users and machine.
5. Cost
The life cycle cost of the machine element consists of production cost, operating cost, maintenance cost and disposal cost.
A machine element should have a minimum possible life cycle cost.
6. Weight
A machine element should have a minimum possible weight.
7. Ergonomics
Ergonomics is defined as the scientific study of the man-machine working environment relationship and the application of anatomical, physiological, and psychological principles to solve the problems arising from the relationship.
The objective of ergonomics is to make the machine fit for user rather than to make the user adopt himself or herself to the machine. If the user is likely to communicate directly with the machine element, it should be designed with ergonomic considerations.
8. Aesthetics
Aesthetics deals with the appearance of the product. In a present day of buyer’s market, with a number of products available in the market are having most of the parameters identical, the appearance of the product is often a major factor in attracting the customer. This is particularly true for consumer durables like automobiles, domestic refrigerators, television, mobile etc.
9. Manufacturing
In a design of machine element, the selection of manufacturing processes must be given a due importance. The manufacturing processes should be selected such that the machine element can be produces with minimum manufacturing cost and as far as possible, with existing manufacturing facilities.
10. Conformance to Standards
A design of machine element should conform to the national and/or international standards and codes.
11. Assembly
A machine element or a product should be designed such that it facilitates to minimize the assembly cost and time.
12. Friction and Wear
Friction and wear are major contributing factors for reducing the life of machine elements and increasing the power loss. The friction can be reduced by improving the surface finish, adequately lubricating the surfaces and replacing the sliding motion by rolling motion. The wear can be reduced by increasing the surface hardness.
13. Life
A machine element should be designed for an adequate life.
14. Vibrations
A machine element should be designed so as to keep the vibrations at minimum level.
15. Thermal considerations
A machine element should be able to withstand the temperature to which it may be subjected. In addition, it should dissipate the heat generated, if any.
16. Lubrication
In the design of machine elements, due considerations must be given for the lubrication of the elements, if there is relative sliding or rolling motion between the elements.
17. Maintenance
A machine element should be such that it can be easily repaired or serviced.
18. Flexibility
A machine element should be flexible so that the modifications can be carried out with minimum efforts.
19. Size and Shape
As far as possible, standard sizes and shaped should be adopted for machine elements
20. Stiffness
Whenever stiffness is a functional requirement like in springs, the machine element should be designed with a precise value of required stiffness.
21. Corrosion
A machine element should be corrosion resistant. This can be achieved by a proper selection of material and adopting the surface coating.
22. Noise
The machine element should be designed such that the noise during operation is at minimum.
References:
Taken from Mechanical Machine Design-I by R. B. Patil.
![clip_image002[6] What is Machine Design](https://engineering.myindialist.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/clip_image0026_thumb.gif)
4 Responses to “Machine design”
Akhil
Good Description. Quite Helpful
admin
Thanks
Namantar
Nicely explained
admin
Thanks