Twenty Three Short Answer Questions on Power Transmission
Question.1. Write the advantages of V-belts over flat belts.
Answer.
- V-belts can transmit more power as compared to flat belts due to wedging action in the grooves.
- These are more suitable for power transmission between two shafts having a short centre distance.
- To compensate for wear or scratch, V-belts require little adjustments.
- By using multiple V-belt system, large power can be transmitted.
- These have longer life and can be easily installed or removed.
- The V-belt drives are smooth as these are made endless.
- The high velocity ratio can be obtained.
- Due to negligible slip between the belt and the pulley, the V-belt drives are positive.
- V-belts give cushioning effect when machines are started.
Question.2. Write the disadvantages of V-belts over flat belts.
Answer.
- The V-belt drives are not suitable for large distance transmission.
- The construction of pulleys for V-belts is more complicated than the flat belts.
- V-belts are not suitable for constant speed application due to certain amount of creep in V-belts.
- The V-belts are not so durable.
- The change in temperature, mismatching of belt lengths and improper belt tension affect the life of V-belt.
Question.3. What is the material used for belts and ropes?
Answer.
The material used for belts and ropes must be strong, flexible and durable. It must have high coefficient of friction. The selection of material is also influenced by climatic as well as service conditions. Usually leather, canvas, cotton and rubber are the materials which are used for flat belts. V-belts are made of rubber impregnated fabric. The material for ropes are cotton, hemp, manila or wire.
Question .4. What are the factors which affect the choice of belt drives?
Answer.
The factors affecting the choice of belt drives are as follows:
- Angular position of the connecting shafts.
- Direction of belt motion.
- Centre distance
- Speed.
Question 5. Name different types of belt drives.
Answer.
The belt drives may be any of the following types:
- Open belt drive,
- Crossed belt drive,
- Angular drive,
- Belt drive with idler pulleys,
- Stepped pulley drive,
- Fast and loose pulley drive,
- Compound drive.
Question.6. Explain open belt drive.
Answer.
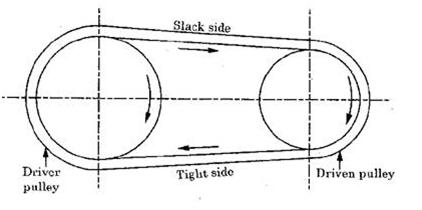
Fig. Open Belt Drive
Fig. shows an open belt drive. In this drive, both the shafts are arranged parallel and rotate in the same direction. This drive is generally used, where the centre distance between the two parallel shafts not more than 8 metres. If the distance is too large, then belt begins to vibrate in a direction perpendicular to the direction of motion which shortens the belts life and there will be a loss of power. In case of very small centre distance, the belt slip increases.
In case of horizontal drives shown in fig. the tension in the lower side is more and is known as tight side , whereas the tension in the upper side is less and is known as slack side.
Question.7. Explain Crossed belt drive.
Answer.
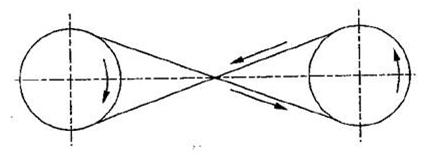
Fig. Crossed Belt Drive
Fig. shows the crossed belt drive. In this case, the shafts are arranged parallel and rotate in opposite direction. If the centre distance remains same, then the angle of contact is more in case of crossed belt drive as compared to open belt drive. So the belt slip, in this drive, is greatly reduced, but the wear and tear is more at a point where the belt crosses.
Question.8. Explain angular belt drive.
Answer.
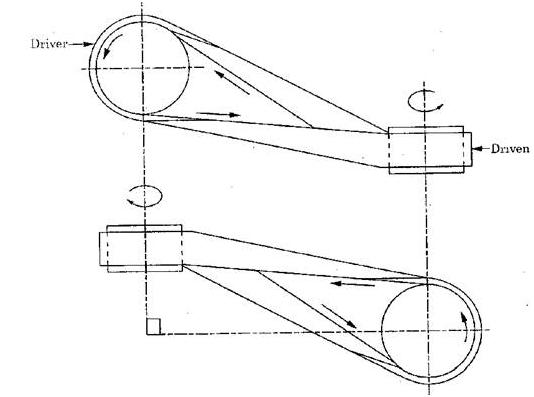
Fig. Angular Drive
In this drive, the axes of rotation of the pulleys connected by the belt may be at right angle or at any other angle which may be intersecting or non-intersecting. When the two connecting pulleys are at right angle, it is known as quarter turn drive shown in fig.
Question.9. Explain belt drive with idler pulleys.
Answer.
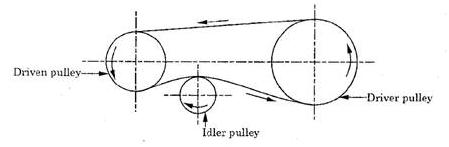
Fig. Belt Drive with Idler pulley
Fig. shows the belt drive with idler pulleys. The drive is used to provide large velocity ratio in short centre distance, thus saving the floor area. The idler pulley is free to rotate on its axis. It presses the belt on the driven side, resulting in the increase of angle contact of the belt. Thus the slippage reduces, hence the belt life increases.
Question 10. Explain stepped pulley drive.
Answer.
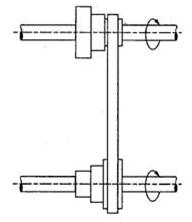
Fig. Stepped pulley drive
This drive shown in figure is used for changing of the angular speed of the driven shaft, while the angular speed of the driving shaft remains constant.
Question.11. Explain fast and loose pulley drive.
Answer.
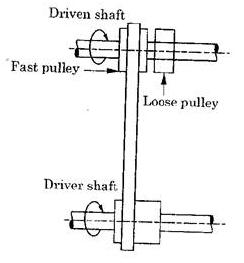
Fig. Fast and Loose Pulley
This drive shown in figure is used when the driven shaft is to be rotated or stopped too often. Two pulleys are mounted on the driven shaft, one of which is keyed on to the shaft and is called fast pulley. The other pulley runs freely on the shaft and is called the loose pulley. When the driven shaft is to be stopped, the belt is pushed on to the loose pulley from fast pulley by means of a lever.
Question.12. Explain compound belt drive.
Answer.
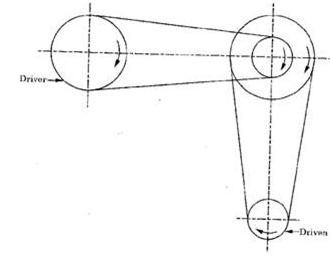
Fig. Compound Belt Drive
The drive shown in fig. is used when large velocity ratio is to be obtained.
Question.13. Explain creep of belt.
Answer.
When a belt passes from tight side to slack side, a certain portion of the belt contracts and it extends again when the belt passes from slack side to tight side. Due to these changes in length, relative motion occurs between the belt and surface of pulley which is known as creep. Due to creep, the speed of driven pulley reduces slightly. After considering the effect of creep, the velocity ratio is given by
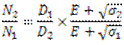
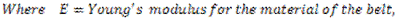
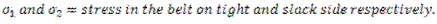
Question.14. Explain crowning of pulleys.
Answer.
If the pulley face is kept flat, then the belt tends to fall off the pulley. To prevent this, the pulley face is never kept flat, but is given a convex curvature. This is called crowning of the pulleys. It helps the belt to run in the centre of the pulley width. The crowning may be conical or rounded off as shown in fig. (a) and fig.(b) respectively.
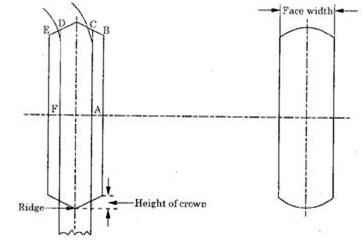
(a) Tapered or Conical Crown (b) Rounded Crown
Fig.
Let us consider tapered or conical crown. Let the belt is in the process of falling off the pulley. Then, the belt stretches more at side AC then at side FE. So, it will be strained on side AC. This strained is opposed by the belt material and the crowning of the pulley helps in automatic adjustment of the belt position, so that the centre line of the belt coincides with the ridge of the crowned surface of the pulley. In other words, with the help of crowning, the belt runs centrally. The amount of crowing is usually kept as 1/96 of the width of the pulley face.
Question.15. Write the expression for the power transmitted by the belts.
Answer.
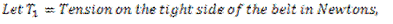
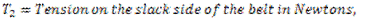
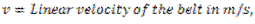
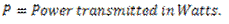
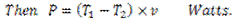
Question.16. Explain initial tension.
Answer.
When a belt is fitted to a pair of pulleys, an initial tension 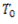 is given to the belt. While transmitting power, the tension of the tight side is increases to
is given to the belt. While transmitting power, the tension of the tight side is increases to 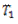 and that on the slack side decreases to
and that on the slack side decreases to 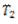 . It is assumed that the material of the belt is perfectly elastic i.e. the strain in the belt is directly proportional to stress in it and the total length of the belt remains unchanged, the tension on the tight side will increase by the same amount as the tension on the slack side decreases.
. It is assumed that the material of the belt is perfectly elastic i.e. the strain in the belt is directly proportional to stress in it and the total length of the belt remains unchanged, the tension on the tight side will increase by the same amount as the tension on the slack side decreases.
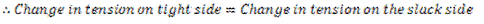
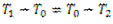
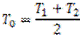
Which shows that the initial tension is the mean of the tension on tight side and slack side of the belt.
Question.17. Write the advantages of rope drives
Answer.
1. These have low cost and operation is economical.
2. These have high mechanical efficiency.
3. The outdoor conditions affect these very little.
4. The shaft may be out of strict alignment.
5. These have smooth, steady and quiet operation irrespective of amount of power transmitted and centre distance.
6. Power may be taken off in any direction and in fractional parts of the whole amount.
Question.18. Write the advantages of gear drive.
Answer.
Gear drive has the following advantages over other transmission devices:
1. Due to short centre distances, gear drive is very compact.
2. It gives positive drive and constant speed ratio.
3. It has high efficiency, reliable service and simple operation.
4. It can be used for precise timing.
5. Its maintenance cost is less and has the longest service life as compared to other mechanical drives.
6. Due to its unlimited sizes, it can take much heavier loads than other drives.
7. It can be used for a wide range of transmission of power i.e. from one-tenths of kW to tens of thousand of kW.
8. It can drive loads subjected to shock at speeds upto 20 m/s.
Question.19. Write the disadvantages of gear drive.
Answer.
Gear drive has the following disadvantages
- It is not suitable for large centre distances because the drive will become bulky.
- Its manufacturing is complex, so special tools and equipments are needed and hence, it is costlier.
- The error and the inaccuracy in the manufacturing may cause undesirable noise and vibrations during operation.
Question.20. Explain worm gear with the help of neat sketch.
Answer.

Fig. Worm and Worm Gear
Reference :http://icons.iconarchive.com/icons/rob-sanders/gear/256/worm-gear-icon.png
Fig. shows the worm gear. In such gears, one gear has screw threads. Due to this factor, these are quiet, vibration free and give a smooth run. These gears are used with shafts angles of 90°. But other angles are also possible. The worm gear is normally the driven member of the pair and is made to wrap around the worm.
Question.21. Draw a neat sketch of simple gear train.
Answer.
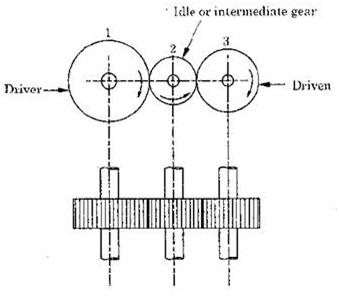
Fig. Simple Gear Train
Question.22. Draw a neat sketch of compound gear train.
Answer.
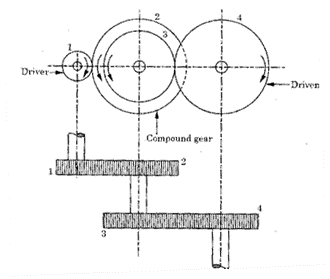
Fig. Compound Gear Train
Question.23. Explain power transmitted by a simple spur gear.
Answer.
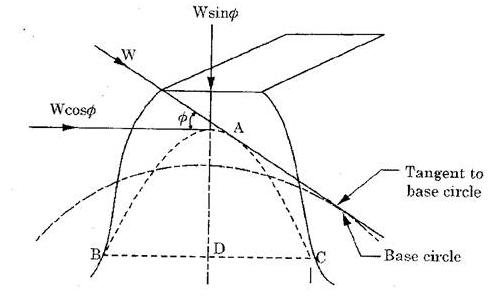
Fig. Power Transmitted by Spur Gear
When power is transmitted by a spur gear, tooth load W acts normal to the profile. The load W can be resolved into two components: 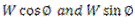 .
.  acts tangentially to the pitch circle and is responsible for transmission of power.
acts tangentially to the pitch circle and is responsible for transmission of power.
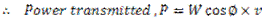
Where 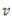 is the pitch line velocity.
is the pitch line velocity.
Now,
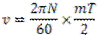
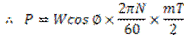
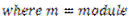
One Response to “Twenty Three Short Answer Questions on Power Transmission”
Upendra
Nice