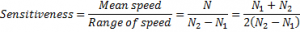Twelve Viva Questions on Governor
Q.1. Define governor.
Answer.
A governor is a device which automatically controls the supply of fuel to the engine. When the load varies and keeps the mean speed within certain limits.
Q.2. Name two types of governor.
Answer.
There are two types of governors:
1. Centrifugal governors,
2. Inertia governors.
Q.3. State the principle of working of centrifugal governor.
Answer.
The centrifugal governor works on the principle of balancing the centrifugal force on the rotating balls by an equal and opposite radial force known as controlling force.
Q.4. Define height of governor.
Answer.
It is the vertical distance from the centre of the governor balls to a point where the axes of the upper arm intersect on the spindle axis. It is denoted by h.
Q.5. Define equilibrium speed in case of governor.
Answer.
It is the speed at which the governor balls are in complete equilibrium and the sleeve does not tend to move in either direction.
Q.6. Define sleeve lift.
Answer.
The vertical distance which the sleeve travel due to change in equilibrium speed is called sleeve lift.
Q.7. Define effort of a governor.
Answer.
The average force which acts on the sleeve for a given percent of change in speed called effort of a governor.
Q.8. Define power of a governor.
Answer.
The power of a governor is defined as the work done at the sleeve for a given percentage of change in speed. It is calculated by the product of effort and displacement of the sleeve.
Q.9. Define sensitiveness of a governor.
Answer.
A governor is said to be sensitive when it readily responds to a small variation in speed.
This may also be defined as the ratio of the mean speed to the change of speed of the governor over its limit of operation.
Q.10. Define hunting of a governor.
Answer.
A governor is said to hunt if the engine speed fluctuates continuously above and below the mean speed. This is caused by a too sensitive governor.
Q.11. Define stability of a governor.
Answer.
A governor is said to be stable if there is only one radius of rotation of the flyballs for the governor equilibrium, for each speed of the engine within the working range.
Q.12. Define isochronisms of a governor.
Answer.
A governor is said to be isochronous if, neglecting friction, the equilibrium speed is the same for all the radii of rotation of balls. This results in infinite sensitivity and the governor will always fly to one or other extreme position. Isochronous governors are unstable.