Long Answer Questions on Vibrations
Q.1. Define vibration. What are its different types? Explain.
Answer.
Vibration
when a particle goes on one side from mean position and returns back and then it goes to other side and again returns back, then it is known as one vibration. In other words, to and fro motion of a particle about a fixed point is known as vibration.
Types of Vibrations
There are three important types of vibrations from subject point of view:
- Free or natural vibrations,
- Damped vibrations,
- Force vibrations.
- Free or natural vibrations : If the vibrations of a particle after giving it an initial displacement remain continued, then the vibrations are called free or natural vibrations. No external force acts on the particle. In other words, the vibrations of the particle with fundamental frequency under the influence of the restoring force are called free vibrations.
- Damped vibrations : The vibrations of a body whose amplitude goes on reducing over every cycle of vibrations are known as damped vibrations. This is due to the fact that a certain amount of energy possessed by the vibrating body is always dissipated in overcoming frictional resistance to the motion.In these vibrations, the amplitude of the vibrations decreases exponentially due to damping forces like frictional force, viscous force, hysteresis etc.
- Forced Vibrations : When the body vibrates under the influence of external periodic force, the n the vibrations are known as forced vibrations.The body does not vibrate with its natural frequency, but it vibrates with the frequency of the driver. The amplitude of the vibrations decreases due to damping forces, but on account of energy gained from the external source, it remains constant. In these vibrations, the amplitude and energy remains constant with respect to the time.
Q. 2. Explain different types of free vibrations.
Answer.
There are three types of free vibrations:
- Longitudinal vibrations,
- Transverse vibrations,
- Torsional vibrations.
Let us consider a weightless bar of length 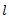 whose one end is fixed and other end carries a disc as shown in fig. The system may have one of the above mentioned three types of free vibrations.
whose one end is fixed and other end carries a disc as shown in fig. The system may have one of the above mentioned three types of free vibrations.
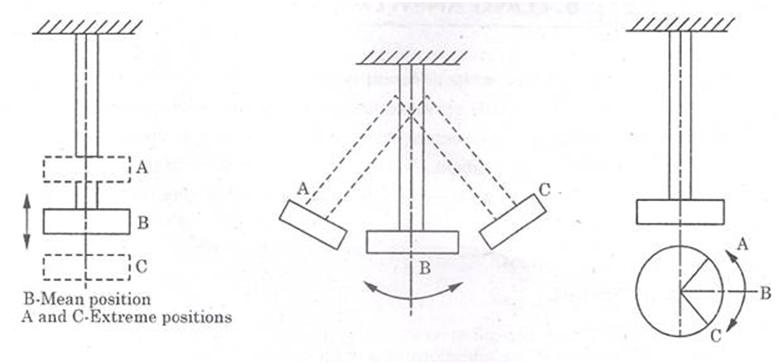
(a) Longitudinal Vibrations (b) Transverse Vibrations (c) Torsional Vibrations
Fig. Types of Free Vibrations
- Longitudinal vibrations : When the particles of a bar or disc move parallel to the axis of the shaft, then the vibrations are known as longitudinal vibrations as shown in fig. (a). The bar is elongated and shortened alternately and thus the tensile and compressive stresses are inducted in the bar. The motion of spring mass system is longitudinal vibrations.
- Transverse Vibrations : When the particles of the bar or disc move approximately perpendicular to the axis of the bar, then the vibrations are known as transverse vibrations as shown in fig.(b). In this case, bar is straight and bent alternately. Bending stresses are induced in the bar.
- Torsional Vibrations : When the particles of the bar or disc get alternately twisted and untwisted on account of vibratory motion of suspended body, it is said to be undergoing torsional vibrations as shown in fig. (c). In this case, torsional shear stresses are induced in the bar.
Q.3. Derive an expression for the natural frequency of free longitudinal vibrations.
Answer.
Natural frequency of Free Longitudinal Vibrations
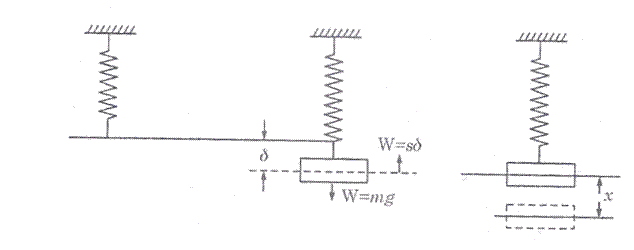
Let us consider a spring mass system as shown in fig. given below.
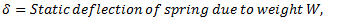
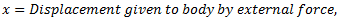
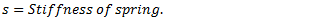
(a) (b) (c)
Fig. Natural Frequency of free Longitudinal Vibrations
From equilibrium position as shown in fig.(b),
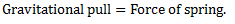
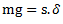
Now, if mass is displaced from its equilibrium position by a distance 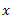 as shown in fig.(c) and released, then
as shown in fig.(c) and released, then
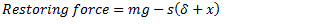
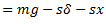
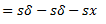
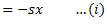
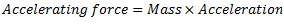
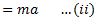
Equating equations (i) and (ii), we get
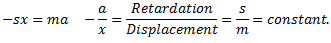
The motion is simple harmonic motion.
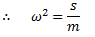
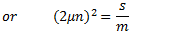
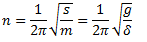
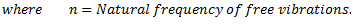
For longitudinal vibrations, the value of static vibration S may be obtained from the relation,
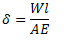
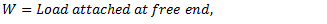
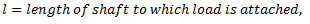
E = Young’s modulus
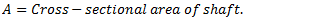
Q.4. Derive an expression for the natural frequency of free transverse vibrations.
Answer. Let us consider a system as shown in fig.

Fig. Natural Frequency of Free Transverse Vibrations
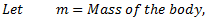
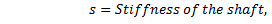
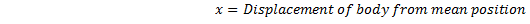
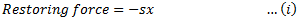
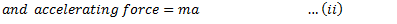
Equating equations (i) and (ii), we get
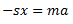
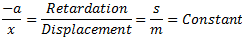
Hence, the natural frequency of free transverse vibrations are same as that of longitudinal vibrations. Therefore,
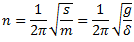
Q.5. Derive an expression for the natural frequency of free torsional vibrations.
Answer.
Let us consider a single rotor system as shown in fig.

Fig. Natural Frequency of Free Torsional Vibrations
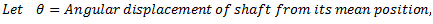
q = Torsional stiffness of shaft
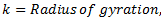
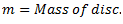
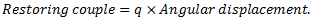
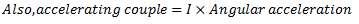
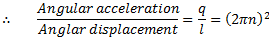
From which,
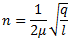
It should be noted that torsional stiffness of shaft may be found out from the following torsional equation:
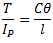
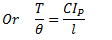
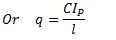
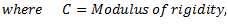
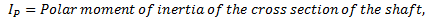
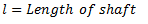
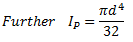
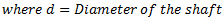
Q.6. What are the causes, harmful effects and remedial measures of vibrations?
Answer.
Causes of Vibrations in machines
For minimizing the undesired vibrations of machines, it is utmost important to find the causes of vibrations in them. The major cause of vibration in machines is unbalancing. So it can also be said that vibrations are the symptoms of unbalance. The basic cause is the non symmetrical mass distribution in various machine components. The various causes of vibrations are listed as below:
- Lack of Compact Soil : If the soil under the foundation of machine is not compact or has settled down being wet or loose, then it may lead to misalignment of the machine which will result in development of vibrations.
- Unbalance Parts : The machine consists of a number of rotating and reciprocating parts having motion in different planes. If these are not dynamically balanced, the unbalanced parts may produce unbalanced forces, which may give rise to unbalanced couples resulting in development of vibrations in machines.
- Loose Fittings : If the machine components are not properly fitted i.e. nuts, bolts and screws including foundation bolts are not properly tightened or they get loosened during operations, then these may lead to development of vibrations in the machines.
- Disturbance due to Vibration Waves : If the heavy machines such as pneumatic hammer, presses,etc. are installed in the near by space, then they produce sound waves due to their working which in turn impinge on the adjoining machines resulting in vibrations in them. A train passing through a plant where a precision machining is being done, may result in vibrations in the machines which may lead to manufacturing defects.
- Effect of Temperature : The temperature may cause changes in structure which increases in vibrations, by bringing critical speed closer to operating speed. Thus a machine which is smooth in cold may be rough when it is hot due to vibrations.
- Hydraulic Vibrations : These may occur from cavitation in pumps. These may be excited by fluid flows and other condition also.
- Manufacturing Defects : The manufacturing defects such as non-symmetry in cast parts, non homogeneity of materials, poor distribution of mass in a completely machined component, variation in mass distribution etc. the causes which will lead to vibrations.
- Lack of Isolation : If the vibrations produced in a machine are not isolated by means of rubber pads or other isolating materials. Between machine and foundation, the vibrations may be transmitted to the adjoining machines also.
- Incorrect Alignment : In a machine, there are many parts fastened together for transmission of power. If the driving and the driven parts are not properly aligned or there is no proper alignment between foundation and the machine, the vibrations may set up in the machine.
Harmful Effects : As discussed earlier in the article that if the vibrations are allowed to exist in the machine parts, the machine produces unwanted noise, high stresses, wear and premature failure of parts. This will not only reduce the efficiency of machines, but also shorten their life. The vibrations are also a great source of human discomfort in the form of physical and mental strain. This adversely effects the working efficiency of the workers.
Remedies
Vibrations can be controlled by
- Removing or controlling or balancing the disturbing forces.
- Changing the natural frequency so that it is far away from the operating frequency of machines so as to avoid resonance.
All the causes of vibrations mentioned above can be corrected to a degree by dynamic and static balancing. Care must be taken for foundations, loose fittings, alignments, soil below foundations etc. The causes which cannot be corrected should be isolated. The natural frequency of a machine can be altered by mounting it on flexible supports. The torsional vibrations can be decreased by decreasing the diameter of the shaft, increasing the length of shaft or using flexible couplings. The natural frequency of shaft can be increased by making it rigid.
Vibration Isolation
If perfect balancing of machine parts is not possible, the various steps for isolating the machine should be taken which are listed below:
- Place the isolators such as springs, rubber pads, felts, glass fibre, lead, asbestos, cork, plastic etc. as the case may be, below the machine.
- If this is not feasible, study should be carried out to increase the weight of the machine.
- Once machine is isolated from the floor, ways to avoid vibrations from transmission through connecting pipes and ducts should be looked into. Fexible connectors, spring hangers and duct wrapping etc. should be used.
- The side air gaps between the foundation and the floor should be provided.
3 Responses to “Long Answer Questions on Vibrations”
BirArmaan Gill
thank you, great article and written in a very chronological, apprehendable and meticulous manner. Please keep posting 🙂 helped me alot.
ABDUL HAMEED
good answer
Nikhil
Nice article but can u write one more lagrarian method