Six Questions on Grinders with Answers
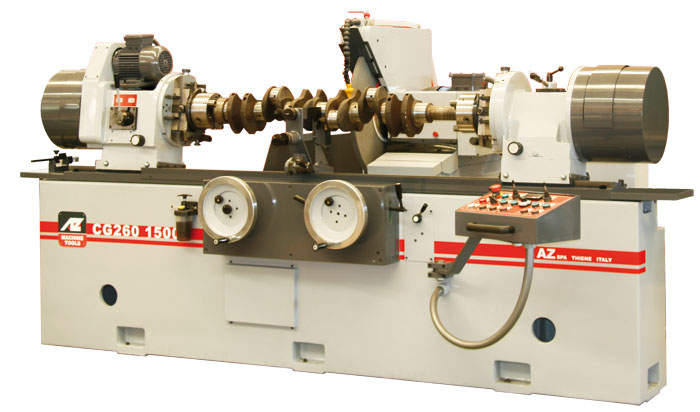
Q.1. Explain crank shaft grinder.
Answer.
Crankshaft or crankpin grinder resembles with cylindrical centre type grinder, but is used to grind the offset pins in the throw of crankshaft.
A crank shaft is held in two indexing pot chucks, one at each end, so that it can be rotated about the axis of its offset pins. The two workheads must allign the ends of the crankshaft accurately and turn in unison.
Interlocks are provided to prevent traverse of the table while grinding, work rotation during wheel dressing, rotation of the work heads with the work unclamped and traverse of the table while workrest shoes are in place.
Crankshaft Grinder
Source: http://www.rtsalesinc.com
Q.2. Explain piston grinder.
Answer.
The grinding of piston of high speed i.c. engines is basically cylindrical grinding, but it deviates slightly from the plain cylindrical grinding.
Many such pistons are not ground truly cylindrical, but slightly elliptical and sometimes, they are slightly tapered. On a piston grinder, a mechanism is attached to move the revolving piston alternately toward and away from the wheel, thus grinding in elliptical form.
At the same time, the work moves progressively away from the wheel during its longitudinal movement, thus grinding the desired taper.

Piston Grinder
Source: http://lovick.com.au
Q.3. Explain way grinder.
Answer.
These are large and heavy single-purpose grinder intended mainly to grind the various surfaces of the ways and beds of machines. The wheel used is cup, ring or segment type mounted on a vertical spindle which can be usually titled at an angle. All sorts of angles may be produced on this machine as shown in fig.
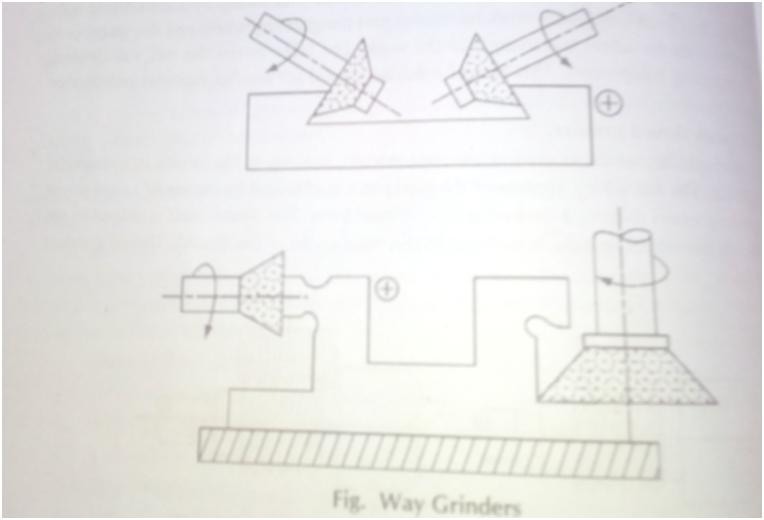
Q.4. Explain tool post grinder.
Answer.
Tool post grinder, sometimes called lathe grinder, is used for miscellaneous and small grinding work on a lathe. It is held on the tool post and fed across the work, longitudinal and cross-wise whenever necessary.
Q.5. Write the functions of cutting fluids used in grinding.
Answer.
Cutting fluids are used in grinding for the following reasons:
- To reduce the excessive heat generated during the operation and to avoid its extreme localization.
- To maintain uniform temperature I order to prevent distortion of the job and breakage of the wheel.
- To drive away the broken abrasive grains and chips, so that they may not scratch against the finished surface and spoil it.
- To prevent the metal chips from clogging into the grain spaces and thus to avoid loading the wheel face.
Q.6. Write safety precautions to be taken in grinding.
Answer.
Safety Precautions to be taken in Grinding are:
- Inspect grinding wheel for cracks before mounting.
- Test grinding wheel for concentricity.
- Check whether all safety guards and hoods are in their place.
- Make a trial run before initial use.
- Use safety goggles.
- Do not exceed the permissible peripheral speed.
- While grinding on the pedestal grinding machine, the tool rest must have a distance of 1-2 mm from the wheel, otherwise the workpiece may get between tool rest and the wheel and break the wheel.
- Do not touch the running grinding wheel.
- Do not remove the protecting covers.
- Clothing of the operator should not come in contact with the wheel and work.


One Response to “Six Questions on Grinders with Answers”
Sam Wilkins
It’s interesting that piston grinders and crank shaft grinders are rather similar to cylindrical grinding. I never realized that tapered end would have a profound effect. Someone recently told me that they all basically were the same. However, after reading your article, they’re not. Thanks for the clarification.