10 Short Answer Questions on Grinding Operation
Q.1. Write the purposes of grinding.
Answer.
Grinding is mainly used for the following purposes:
- It is used for sharpening the cutting tools.
- It is used for grinding threads in order to have close tolerances and better finish.
- It is used to produce surfaces with a higher degree of smoothness.
- It is used to machine materials which are too hard for machining by other methods using cutting tools.
- Sometimes, it is also used for higher material removal rate.
Q.2. Name different bonds used in the manufacturing of grinding wheels
Answer:
The bonds commonly used for manufacturing of grinding wheels are as follows:
(i) Vitrified bond (denoted by V),
(ii) Silicate bond (denoted by s),
(iii) Shellac bond (denoted by E),
(iv) Rubber bond (denoted by R),
(v) Bakelite or resinoid bond (denoted by B),
(vi) Oxychloride bond.
Q.3. Write the advantages of built up wheels.
Answer.
Built up wheels are mainly used in surface grinding and have following advantages:
- It is easier to manufacture these wheels in large sizes in comparison to the solid wheels of same sizes.
- These cut intermittently and hence cool grinding is the result.
Q.4. Explain testing of grinding wheels.
Answer.
The grinding wheels should be first examined for any flaw, and other defect before it is fastened to the spindle. If any crack or serious flaw is observed, it should never be used as it may get fractured under stressed condition. Thus the grinding wheel has to be examined for cracks by sound test.
Vitrified and silicate wheels when freely suspended must give a clear sound on knocking with a mallet. Small wheels can be held freely with the hole in finger and tapped gently with a plastic hammer or handle of screw driver etc. at a point approximately 45 deg from the vertical centre line.
Q.5. Explain balancing of grinding wheels.
Answer.
If the centre of gravity of a grinding wheel and its axis of rotation coincide, the grinding wheel is said to be balanced.
The process of ensuring uniform distribution of the mass on the grinding wheel around its axis so that no unbalanced force acts on it during its rotation is called balancing of the grinding wheel.
A balanced grinding wheel operates reliable at high peripheral speeds. An unbalanced grinding wheel produces chatter and leaves undue strain on the machine. The problem becomes serious in the wheels of large diameter and needs attention. The unbalancing of grinding wheels occurs due to following reasons:
- Non-uniform density of the wheel material.
- Incorrect mounting of the grinding wheel.
- Incorrect shape of the wheel.
- Eccentricity in the wheel hole with reference to the wheel surface.
Q.6. Name different types of rough grinders.
Answer.
Most commonly used rough grinders are as follows:
- Floor stand and bench grinder.
- Portable and flexible shaft grinder.
- Swing belt grinder.
- Abrasive belt grinder.
Q.7. Write the advantages of internal centreless grinding.
Answer.
The advantages of internal centreless grinding are as follows:
- The main advantage of centreless grinding is its high productivity.
- There is no need of centering and use of fixtures is totally avoided.
- It can be applied for both internal as well as external grinding.
- The work is rigidly supported and hence there is no chatter or deflection of the work.
- The operation is easy and hence less skilled worker is required.
- Size of work is easily controlled.
- Large grinding wheels are used and hence errors due to wheel wear are reduced.
- Maintenance required is very less.
Q.8. Write the disadvantages of internal centreless grinding.
Answer.
The main disadvantages of internal centreless grinding are as follows:
- Work with flats and keyways cannot be ground.
- In hollow work, there is no assurance that the outer diameter wil be concentric to the inner one.
- Work having several diameters is not easily handled.
Q.9. Explain Roll Grinder.
Answer.
A roll grinder is a cylindrical grinder of 500 to 900 mm swing by 2.5 to 5 m length between centres.
It is built either with work traversing past the grinding wheel and the wheel in a fixed position or with the wheel traversing past the work.
The table carries the roll, roll driving and the roll supporting equipments. This type of machine is used for smaller diameter and shorter length rolls.
Figure: A Roll Grinder (Source)
Q.10. Explain thread grinder.
Answer.
Thread grinder, which is used to generate threads, belongs to the family of cylindrical grinding machines. The traversing motion of the workpiece is obtained by means of lead screw so that the grinding wheel follows a desired helix or thread form. The wheel itself is shaped to the thread profile and the wheel spindle is inclined to the helix angle of the thread. Thread grinders are shown in fig.
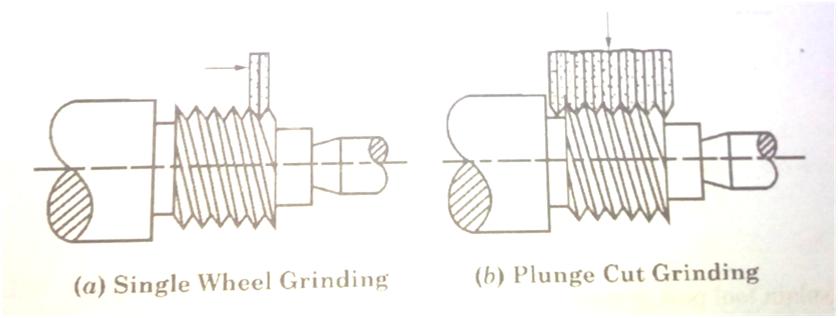
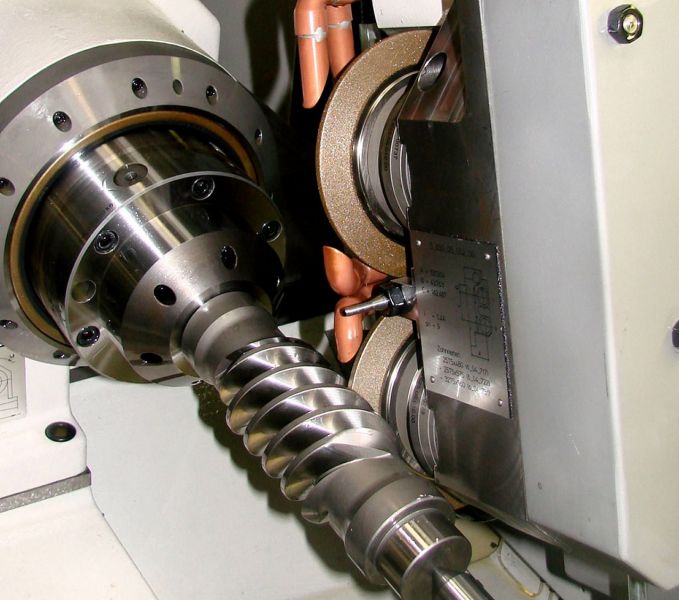 Figure: A Thread Grinder (Source)
Figure: A Thread Grinder (Source)

One Response to “10 Short Answer Questions on Grinding Operation”
Hannah Schroeder
This article was really helpful, especially the part that listed the purposes of a cylindrical grinding machine. I didn’t know that you could use it to sharpen cutting tools. I’d imagine that cutting tools can get blunt really easily if they’re used a lot, and blunt edges might ruin the craftsmanship and make it less precise. It might be handy to have a grinding machine nearby so you can sharpen the edges if they get dull.