Question.1. The load required to produce a unit deflection in the spring is called
(a) Modulus of Rigidity
(b) Spring stiffness
(c) Flexural rigidity
(d) Tensional rigidity
Question.2. In spring balances, the spring is used
(a) To apply forces
(b) To absorb shocks
(c) To store strain energy
(d) To measure forces
Question.3. The most important property for the spring material is
(a) High elastic limit
(b) High deflection value
(c) Resistance to fatigue and shock
(d) All of these
Question.4. The springs in brakes and clutches are used
(a) To apply forces
(b) To measure forces
(c) To absorb shocks
(d) To absorb strain energy
Question.5. In a watch, the spring is used to store energy. The energy is released
(a) To stop the watch
(b) To run the watch
(c) To change the time
(d) All of these
Question.6. A spring used to absorb shocks and vibrations is
(a) Close-coil helical spring
(b) Open coiled helical spring
(c) Spiral spring
(d) Leaf spring
Question.7. The spring used in mechanical toys is
(a) Leaf spring
(b) Spiral spring
(c) Helical spring
(d) All of these
Question.8. The laminated springs are given initial curvature
(a) To have uniform strength
(b) To make it more economical
(c) So that plates may become flat, when subjected to design load
(d) None of these
Question.9. If a close-coiled helical spring is subjected to load W and the deflection produced is 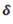 , then stiffness of the spring is given by
, then stiffness of the spring is given by
(a) 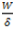
(b) 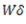
(c) 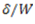
(d) 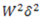
Question.10. When a close-coiled helical spring is subjected to an axial load, it is said to be under.
(a) Bending
(b) Shear
(c) Torsion
(d) Crushing
Question.11. The close-coiled helical springs ‘A’ and ‘B’ are of same material, same coil diameter, same wire diameter and subjected to same load. If the number of turns of spring ‘A’ is half that of spring ‘B’, the ratio of deflection of spring ‘A’ to spring ‘B’ is
(a)1/2
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 4
Question.12. In the above question, the ratio of stiffness of spring A to spring B is
(a) 1/2
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 4
Question.13. A close –coiled helical spring is cut into two equal parts. The stiffness of the resulting springs will be
(a) same
(b) double
(c) half
(d) One-fourth
Question.14. Two close-coiled helical springs are equal in all respects except the number of turns. If the number of turns are in the ratio of 2:3, then the stiffness of the spring will be in the ratio of
(a) 2:3
(b) 4:9
(c) 3:2
(d) 9:4
Question.15. The equivalent spring constant is
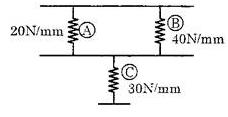
(a) 20 N/mm
(b) 30 N/mm
(c) 45 N/mm
(d) 90 N/mm
Question.16. A tensional bar with a spring constant ‘K’ is cut into ‘n’ equal lengths. The spring constant of each new portion is
(a) 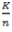
(b) 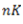
(c) 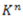
(d) 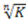
Question.17. A close-coiled helical spring of stiffness 30 N/mm is arranged in series with another such spring of stiffness 60 N/mm. The stiffness of composite unit is
(a) 20 N/mm
(b) 30 N/mm
(c) 45 N/mm
(d) 90 N/mm
Question.18. Two close-coiled helical spring of stiffness 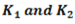 are connected in parallel. The combination is equivalent to a single spring of stiffness
are connected in parallel. The combination is equivalent to a single spring of stiffness
(a) 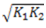
(b) ![]()
(c) 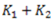
(d) ![]()
Question.19. If a close-coiled helical spring absorbs 50 N-mm of energy while extending by 5 mm, its stiffness will be
(a) 2 N/mm
(b) 4 N/mm
(c) 6 N/mm
(d) 10 N/mm
Question.20. A helical spring of constant k is cut into four equal pieces and the four pieces are then combined in parallel. The equivalent spring constant will be
(a) k/16
(b) k/4
(c) 4k
(d) 16k
Answers
1. (b) 2.(d) 3. (d) 4. (a) 5. (b) 6. (d) 7. (b)
8. (c) 9. (a) 10. (c) 11. (a) 12. (c) 13. (b) 14. (c)
15.(a) 16. (b) 17. (a) 18. (c) 19. (d) 20. (d)
3 Responses to “Twenty MCQ’s on Springs”
mukesh verma
it is really so helpful….
mukesh verma
it was so helpful
Er.S K Paul
it will be better if all types of springs are included .