Thirty Five MCQ’s on Stress AND Strain
Question.1. The deformation per unit length is called
(a) Strain
(b) Stress
(c) Elasticity
(d) None of these
Question.2. The ability of the material to deform without breaking is called
(a) Elasticity
(b) Plasticity
(c) Creep
(d) None of these
Question.3.Which of the following material is more elastic?
(a) Rubber
(b) Glass
(c) Steel
(d) Wood
Question.4. The percentage elongation and the percentage reduction in area depends upon
(a) Tensile strength of the material
(b) Ductility of the material
(c) Toughness of the material
(d) None of these
Question.5. The property of a material by which it can be beaten or rolled into thin sheets, is called
(a) Elasticity
(b) Plasticity
(c) Ductility
(d) Malleability
Question.6. A bar of square cross section of side ‘a’ is subjected to a tensile load P on a plane inclined at 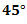 to the axis of the bar, the normal stress will be.
to the axis of the bar, the normal stress will be.
(a) ![]()
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]()
(d) ![]()
Question.7. A load of 1 kN acts on a bar having cross-sectional area 0.8 cm2 and length 10 cm. The stress developed in the bar is
(a) 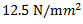
(b) 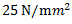
(c) 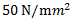
(d) 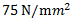
Question.8. A steel bar 100 mm long is subjected to a tensile stress 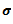 .If the change in length of the bar is
.If the change in length of the bar is 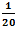 mm, what will be the value of
mm, what will be the value of 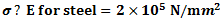 .
.
(a) 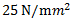
(b) 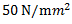
(c) 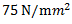
(d) 100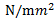
Question.9. The property of a material by which it can be drawn to a smaller section by applying a tensile load is called
(a) Elasticity
(b) Plasticity
(c) Ductility
(d) Malleability
Question.10. If a material has identical properties in all directions, it is called
(a) Elastic
(b) Plastic
(c) Isotropic
(d) Homogeneous
Question.11. The stress at which extension of a material takes place more quickly as compared to increase in load, is called
(a) No elastic zone
(b) Plastic point
(c) Yield point
(d) Breaking point
Question.12. A brittle material has
(a) No elastic zone
(b) No plastic zone
(c) Large plastic zone
(d) None of these
Question.13. Every material obeys the Hooke’s law within
(a) Elastic limit
(b) Plastic limit
(c) Limit of proportionality
(d) None of these
Question.14. Units of strain
(a) 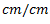
(b) 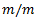
(c) 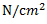
(d) No unit
Question.15. The increase in the length of a bar of length 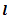 area
area 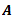 , modulus of elasticity E due to a tensile load
, modulus of elasticity E due to a tensile load 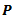 is given by
is given by
(a) ![]()
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]()
(d) ![]()
Question.16. The ratio of lateral strain to linear strain is called
(a) Modulus of Elasticity
(b) Modulus of Rigidity
(c) Bulk Modulus
(d) Poisson’s Ratio
Question.17. Dimensional formula for Young’s modulus of elasticity is
(a) 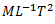
(b) 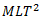
(c) 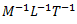
(d) 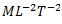
Question.18. A perfectly elastic body
(a) Can move freely
(b) Has perfectly smooth surface
(c) Is not deformed by any external surface
(d) Recovers its original size and shape when the deforming force is removed.
Question. 19. The value of Poison’s ratio depends upon
(a) Nature of load, tensile or compressive
(b) Magnitude of load
(c) Material of the test specimen
(d) Dimensions of the test specimen
Question. 20. When a section is subjected to two equal and opposite forces tangentially to the section, the stress produced is known as
(a) Tensile stress
(b) Lateral stress
(c) Shear stress
(d) No stress
Question.21. Which of the following is a dimensionless quantity?
(a) Shear stress
(b) Poison’s ratio
(c) Strain
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Question.22. Percentage elongation during tensile test is indication of
(a) Ductility
(b) Malleability
(c) Creep
(d) Rigidity
Question.23. Brittleness is opposite to
(a) Toughness
(b) Plasticity
(c) Malleability
(d) None of these
Question.24. The statement : stress is proportional to strain, i.e. the Hooke’s law holds good upto
(a) Elastic Limit
(b) Proportional Limit
(c) Plastic Limit
(d) Yield point
Question.25. The limit beyond which the material does not behave elastically is known as
(a) Proportional limit
(b) Elastic limit
(c) Plastic limit
(d) Yield Point
Question.26. When mild steel is subjected to a tensile load, its fracture will conform to
(a) Star shape
(b) Granular shape
(c) Cup and cone shape
(d) Fibrous shape
Question.27. When a wire is stretched to double in length, the longitudinal strain produced in it is
(a) 0.5
(b) 1.0
(c) 1.5
(d) 2.0
Question.28. The length of a wire is increased by 1 mm on the application of a certain load. In a wire of the same material but of twice the length and half the radius, the same force will produce an elongation of
(a) 0.5 mm
(b) 2 mm
(c) 4 mm
(d) 8 mm
Question.29. A cylindrical rod of length 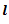 and diameter
and diameter 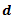 is rigidly fixed at its upper end and hangs vertically. The elongation produced in the rod due to its self weight W is
is rigidly fixed at its upper end and hangs vertically. The elongation produced in the rod due to its self weight W is
(a) ![]()
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]()
(d) ![]()
Question.30. The Young’s modulus E, the shear modulus G and the Poisson’s ratio 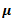 for a material are related by the expression
for a material are related by the expression
(a) 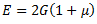
(b) 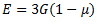
(c) 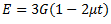
(d) 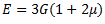
Question.31. The elastic constant E, G and K are related by the expression
(a) ![]()
(b) ![]()
(c) ![]()
(d)![]()
Question.32. The independent elastic constants for a homogeneous and isotropic material are
(a) 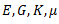
(b) 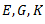
(c) 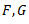
(d) 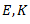
Question.33. When a bar is subjected to a change of temperature and its longitudinal deformation is prevented, the stress induced in the bar is
(a) Tensile
(b) Compressive
(c) Shear
(d) Temperature
Question.34. When a bar is subjected to increase in temperature and its deformation is prevented, the stress induced in the bar is
(a) Tensile
(b) Compressive
(c) Shear
(d) None of the above
Question.35. In a composite body, consisting of two different materials………..will be same in both materials.
(a) Stress
(b) Strain
(c) Both stress and strain
(d) None of these
Answers
1. (a) 2.(b) 3. (c) 4. (b) 5. (d) 6. (b) 7. (a)
8. (d) 9. (c) 10. (c) 11. (c) 12. (b) 13. (c) 14. (d)
15.(b) 16. (d) 17. (a) 18. (d) 19. (c) 20. (c) 21. (d)
22. (a) 23. (b) 24. (b) 25. (b) 26. (c) 27. (b) 28. (d)
29. (b) 30. (a) 31. (d) 32. (a) 33. (d) 34. (b) 35. (b)
3 Responses to “Thirty Five MCQ’s on Stress AND Strain”
Nehal
Mcq:17 m1 l(-1) t(-2)
Nishant
It’s very nice
UNIQUE BAKHREL
MCQ 32. For Homogeneous and isotropic material have two independent elastic constant.