GATE Solved Questions on Basics of Thermodynamics
Basic Thermodynamics is a very important topic for the GATE Preparation. Here are Some GATE questions based on the basic thermodynamics. The questions are accompanied with hints, solutions and answers.
Question 1. A small steam whistle (perfectly insulated and doing no shaft work) causes a drop of 0.8 kJ/kg in enthalpy of steam from entry to exit. The kinetic energy of the steam at entry is negligible, the velocity of steam at exit is
(A) 4 m/s
(B) 40 m/s
(C) 80 m/s
(D) 120 m/s
GATE-ME-2001
HINT 1. (Ans B)
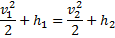
Here 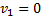 , therefore
, therefore
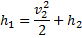
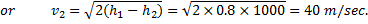
Question 2. What is the speed of sound in Neon gas at a temperature of 500 K (gas constant of neon is 0.4210 kJ/kg-k)?
(A) 492 m/s
(B) 460 m/s
(C) 592 m/s
(D) 543 m/s
GATE-ME-2002
Hint 2. (Ans D)
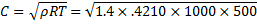

Question 3. A reversible thermodynamic cycle containing only three processes and producing work is to be constructed. The constraints are
(i) There must be one isothermal process,
(ii) There must be one isentropic process,
(iii) The maximum and minimum cycle pressure and the clearance volume are fixed,
(iv) Polytropic processes are not allowed.
Then the number of possible cycles are
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
GATE-ME-2005
Hint 3. (Ans D)
2 cycles having constant volume process (i, ii) and 2 cycles having constant pressure process (iii, iv) can be formed.
Question 4. The following four figures have been drawn to represent a fictitious thermodynamic cycle, on the P-V and T-S planes.
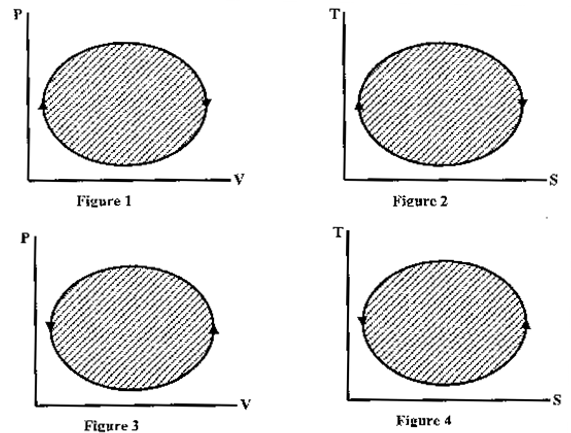
According to the first law of thermodynamics, equal areas are enclosed by
(A) Fig 1 and 2
(B) Fig 1 and 3
(3) Fig 1 and 4
(4) Fig 2 and 3
GATE-ME-2005
Hint 4. (Ans A)
Clockwise devices are heat engines and anti-clockwise devices are heat pumps or refrigerators.
Statement for linked Answer Question 5 & 6.
A football was inflated to a gauge pressure 1 bar when the ambient temperature was 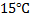 . When the game started next day, the air temperature at the stadium is
. When the game started next day, the air temperature at the stadium is 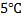 . Assume that the volume of the ball remains constant at
. Assume that the volume of the ball remains constant at 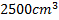
Question 5. The amount of the heat lost by the air in the football and the gauge pressure of air in the football at the stadium respectively is
(A) 30.6 J, 1.94 bar
(B) 21.8, 0.93 bar
(C) 61.1 J, 1.94 bar
(D) 43.7 J, 0.93 bar
GATE-ME-2006
Hint 5. (Ans D)
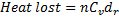
Question 6. Gauge pressure of air to which the ball must have been originally inflated so that it would equal 1 bar gauge at the stadium is
(A) 2.23 bar
(B) 1.94 bar
(C) 1.07 bar
(D) 1.00 bar
GATE-ME-2006
Hint 6. (Ans C)
Question 7. Which of the following relationship is valid only for reversible process undergone by a closed system of simple compressible substance (neglect changes in kinetic and potential energy)?
(A) 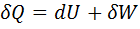
(B) 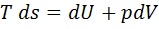
(C) 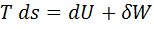
(D) 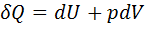
GATE-ME-2007
Hint 7. (Ans C)
For reversible process, by first law
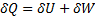
Also by definition of entropy, dS=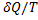
Hence 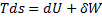
Question 8. In a steady state flow process taking place in a device with a single inlet and a single outlet, the work done per unit mass flow rate is given by 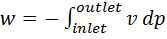 , where
, where 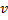 is the specific volume and p is the pressure. The expression for w given above
is the specific volume and p is the pressure. The expression for w given above
(A) is valid only if the process is both reversible and adiabatic
(B) Is valid only if the process is both reversible and isothermal
(C) Is valid for any reversible process
(D) Is incorrect; it must be 
GATE-ME-2008
Hint 8. (Ans C)
For steady flow process,
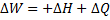
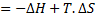
But for reversible process,
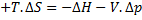
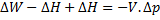
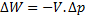
For steady flow reversible process, ![]()
Question 9. A rigid, insulated tank is initially evacuated. The tank is connected with a supply line through which air (assumed to be ideal gas with constant specific heats) passes at 1 MPa,  . A valve connected with the supply line is opened and the tank is charged with air until the final pressure inside the tank reaches 1 MPa. The final temperature inside the tank
. A valve connected with the supply line is opened and the tank is charged with air until the final pressure inside the tank reaches 1 MPa. The final temperature inside the tank
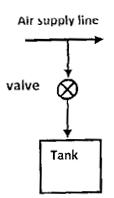
(A) Is greater than 
(B) Is less thsn 
(C) Is equal to 
(D) May be greater than, less than, or equal to  , depending on the volume of the tank
, depending on the volume of the tank
GATE-ME-2008
Hint 9. (Ans. A)
The fixed temperature inside the tank is given by 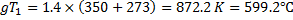
Question 10. A balloon containing an ideal gas is initially kept in an evacuated and insulated room. The balloon ruptures and the gas fills up the entire room. Which one of the following statement is true at the end of the above process?
(A) The internal energy of the gas decreases from its initial value, but the enthalpy remains constant
(B) The internal energy of the gas increases from its initial value, but the enthalpy remains constant
(C) Both internal energy and enthalpy of the gas remains constant
(D) Both internal energy and the enthalpy of the gas increase
GATE-ME-2008
Hint 10. (Ans C)
Since the kinetic energy of the molecules won’t change in vacuum,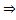 temperature remains constant.
temperature remains constant.
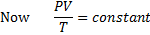
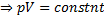
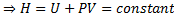
Question 11. A compressor undergoes a reversible, steady flow process. The gas at inlet and outlet of the compressor is designated as state 1 and state 2 respectively. Potential and kinetic energy changes are to be ignored. The following notations are used:
V=specific volume and P= pressure of the gas.
The specific work required to be supplied to the compressor for this gas compression process is
(A) 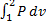
(B) 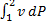
(C) 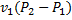
(D) 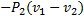
GATE-ME-2009
Hint 11. (Ans B)
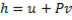
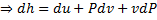
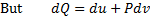
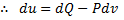
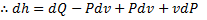
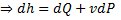
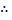
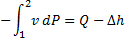
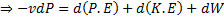
Since the potential energy and the kinetic energy are constant .
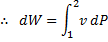
Question 12. Heat and work are
(A) Intensive properties
(B) Extensive properties
(C) Point functions
(D) Path functions
GATE-ME-2011
Hint 12. (Ans D)
Heat and work are path functions.
Question 13. The contents of a well- insulated tank are heated by a resistor of 23 Ω in which 10 A current is flowing. Consider the tank with its contents as a thermodynamic system. The work done by the system and the heat transfer to the system are positive. The rates of heat (Q), work (W) and change in (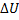 ) during the process in KW are
) during the process in KW are
(A) Q=0, W=-2.3,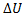 =+2.3
=+2.3
(B) Q=+2.3, W=0, 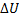 =+2.3
=+2.3
(C) Q=-2.3, W=0, 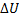 =-2.3
=-2.3
(D) Q=0, W=2.3, 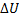 =-2.3
=-2.3
GATE-ME-2011
Hint 13. (Ans B)
Heat added to the contents of the system.
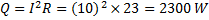
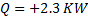
No work is done by the system , 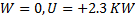
Question 14. Steam enters an adiabatic turbine operating at steady state with an enthalpy of 3251.0 kJ/kg respectively. The mass flow rate of steam is 10 kg/s. kinetic and potential energy changes are negligible. The power output of the turbine in MW is
(A) 6.5
(B) 8.9
(C) 9.1
(D) 27.0
GATE-ME-2012
Hint 14. (Ans B)
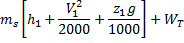
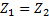
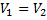
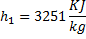
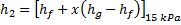
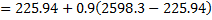
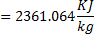
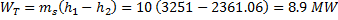
Statement for Linked Answer Question 15 and 16
Air enters an adiabatic nozzle at 300 kPa, 500 K with a velocity of 10 m/s. it leaves the nozzle at 100 kPa with a velocity of 180 m/s. The inlet area is 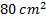 . The specific heat of air
. The specific heat of air 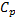 is 1008 J/kg K
is 1008 J/kg K
Question 15. The exit temperature of the air is
(A) 516 K
(B) 532 K
(C) 484 K
(D) 468 K
GATE-ME-2012
Hint 15. (Ans C)
Question 16. The exit area of the nozzle in 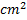 is
is
(A) 90.1
(B) 56.3
(C) 4.4
(D) 12.9
GATE-ME-2012
Hint 16.(Ans D)
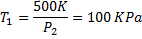
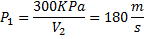
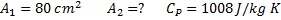
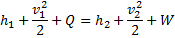
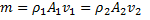
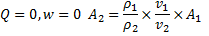
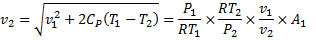
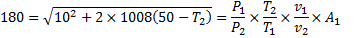
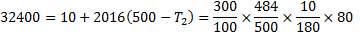
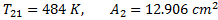
Question 17. A cylinder contains 5 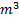 of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 bar. This gas is compressed in a reversible isothermal process till its pressure increases to 5 bar. The work in kJ required for this process is
of an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 bar. This gas is compressed in a reversible isothermal process till its pressure increases to 5 bar. The work in kJ required for this process is
(A) 804.7
(B) 953.2
(C) 981.7
(D) 1012.2
GATE-ME-2013
Hint 17. (Ans A)
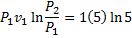
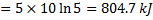
Question 18. Specific enthalpy and velocity of steam at inlet and exit of a steam turbine running under steady state are as given below:
Specific enthalpy (kJ/kg) |
Velocity (m/s) |
|
Inlet steam condition |
3250 |
180 |
Exit steam condition |
2360 |
5 |
The rate of heat loss from the turbine per kg of steam flow rate is 5 kW. Neglecting changes in potential energy of steam, the power developed in kW by the steam turbine per kg of steam flow rate, is
(A) 901.2
(B) 911.2
(C) 17072.5
(D) 17082.5
GATE-ME-2013
Hint 18. (Ans A)
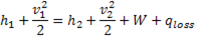
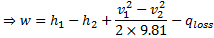
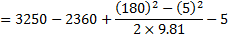
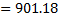
Question 19. The pressure, temperature and velocity of air flowing in a pipe are 5 bar, 500 K and 50 m/s, respectively. The specific heats of air at constant pressure and at constant volume are 1.005 kJ/kg K and 0.718 kJ/kg K respectively. Neglect potential energy. If the pressure and temperature of the surrounding are 1 bar, 300 K respectively, the available energy in kJ/kg of the air steam is
(A) 170
(B) 191
(C) 187
(D) 213
GATE-ME-2013
Hint 19. (Ans B)
Available energy in difference in availability
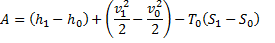
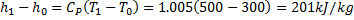
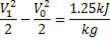
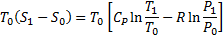
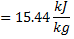
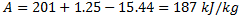
Answer keys
1. (B) 2. (D) 3. (D) 4. (A) 5. (D) 6. (C) 7. (C) 8. (C) 9. (A) 10. (C) 11. (B) 12. (D) 13. (B) 14. (B) 15. (C) 16. (D) 17. (A) 18. (A) 19 (B)
10 Responses to “Previous Years GATE Solved MCQs on Basics of Thermodynamics”
Divesh
In question no.14 no data is provided to calculate h2. so how have you calculated it??
in question no. 19 you have solved the answer to option (C) but have marked option (b) as correct answer. so what’s the correct answer out of the two??
Aswin
Thank you send More
pratik chandra
its really useful please try to send more question of recent few years
Rakesh
QUESTION 2 : THE GAMMA WHICH IS REPRESENTED BY RO IN THE HINT.. SHOULD BE 1.667 AS NEON IS A NOBLE GAS , MONOATOMIC GASES HAVE ADIABATIC INDEX AS 1.667.. AND THE ANSWER IS 592M/S
ravi
in que 7 c ans is for both irrev and rev bcoz it is properties relationship but i think option d is more preferable bcz pdv is written only for rev process in 1st law
naresh namballa
please explain questions 5&6 clearly i haven’t understood
Ankit Raj
Q 6 both A and C are correct.. dS =dQ/t
So for reversible process dQ=dU+dW
also dS*T= dU+dW
there are lots of mistakes in calculation and answer of question no. 13 is wrong in your given hint.
pls do corrections in this list of answers and hints of them
Prashant gunjeti
In Q7) ans is 4
Option 1 ) first law of thermodynamics doesnt tell about process is reversible or irreversible it is valid for both. also it valid for open or closed system
Option2)it is the relation of properties hence equation valid for rev. &Irrev , open &close system
Option3) relation of property and path function valid for rev &irrev , open &closed system
Option 4) it is relation of property and path fu
DelQ- path fun ,du – point fun ,pdv – rev process& closed system..
admin
Thanks for the comment. Someone please check this comment.