Solved GATE Questions on Fluid Dynamics
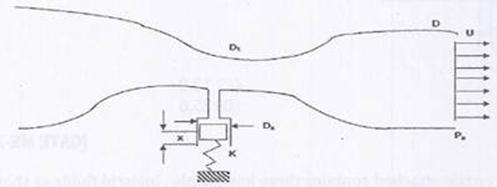
Question 1. Air flow through a venturi and into atmosphere. Air density is 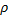 ; atmospheric pressure is
; atmospheric pressure is 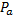 ; throat diameter is
; throat diameter is 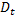 ; exit diameter is D and exit velocity is U. The throat is connected to a cylinder containing a frictionless piston attached to a spring. The spring constant is k. The bottom surface of the piston is exposed to atmosphere. Due to the flow, the piston moves by distance x. Assuming incompressible frictionless flow, x is
; exit diameter is D and exit velocity is U. The throat is connected to a cylinder containing a frictionless piston attached to a spring. The spring constant is k. The bottom surface of the piston is exposed to atmosphere. Due to the flow, the piston moves by distance x. Assuming incompressible frictionless flow, x is
(A) 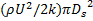
(B) 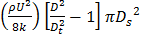
(C) 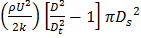
(D) 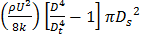
GATE-ME-2003
Hint 1. (Ans D)
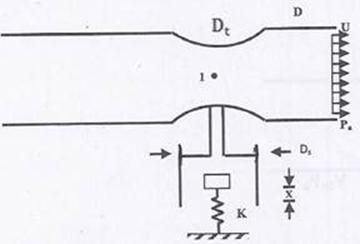
Applying Bernoulli’s equation at point (1) and (2), we have
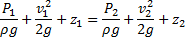
Since venturi is horizontal
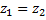
Now
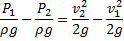
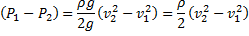
Since 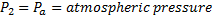
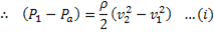
Applying continuity equation at points (i) and (ii), we have
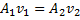
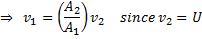
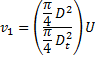
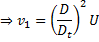
From equation (i)
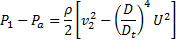
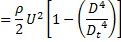
At point P
Spring force=pressure force due to air
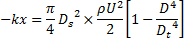
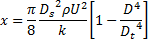
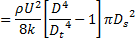
Question 2. A venturimeter of 20 mm throat diameter is used to measure the velocity of water in a horizontal pipe of 40 mm diameter. If the pressure difference between the pipe and throat sections is found to be 30 kPa then, neglecting frictional losses, the flow velocity is
(A) 0.2 m/s
(B) 1.0 m/s
(C) 1.4 m/s
(D) 2.0 m/s
GATE-ME-2005
Hint 2. (Ans D)
We know,
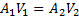
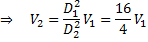
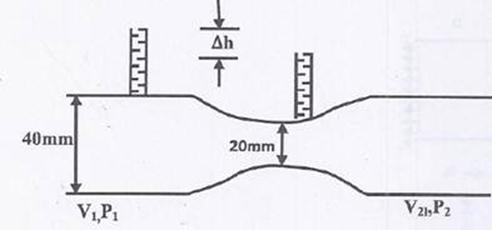
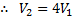
Applying Bernoulli’s Equation
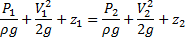
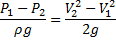
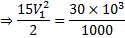
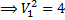
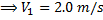
Question 3. In a steady flow through a nozzle, the flow velocity on the nozzle axis is given by 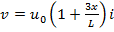 , where x is the distance along the axis of the nozzle from its inlet plane and L is the length of the nozzle. The time required for a fluid particle on the axis to travel from the inlet to the exit lane of the nozzle is
, where x is the distance along the axis of the nozzle from its inlet plane and L is the length of the nozzle. The time required for a fluid particle on the axis to travel from the inlet to the exit lane of the nozzle is
(A) 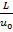
(B) 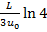
(C) 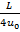
(D) 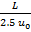
GATE-ME-2007
Hint 3. (Ans B)

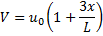
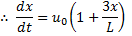
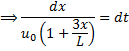
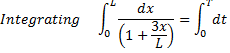
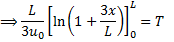
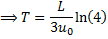
Question 4. A smooth pipe of diameter 200 mm carries water. The pressure I the pipe at section S1 (elevation : 10 m) is 50 kPa. At section S2 (elevation : 12 m) the pressure is 20 kPa and velocity is 2 m/s. Density of water is 1000 kg/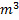 nd acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/
nd acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/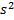 . Which of the following is TRUE
. Which of the following is TRUE
(A) Flow is from S1 to S2 and head loss is 0.53 m
(B)Flow is from S2 to S1 and head loss is 0.53 m
(C) Flow is from S1 to S2 and head loss is 1.06 m
(D) Flow is from S1to S2 and head loss is 0.63 m
GATE-ME-2010
Hint 4. (Ans C)
Apply Bernoulli’s theorem
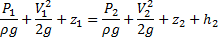
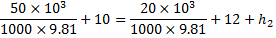
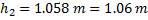
Heat loss occurs in the direction 1-2.
 Flow is from
Flow is from  and head loss is 1.06 m
and head loss is 1.06 m
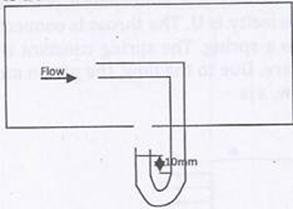
Question 5. Figure shows the schematic for the measurement of velocity of air (density = 1.2 kg/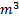 ) through a constant area-duct using a pitot tube and water-tube manometer. The differential head of water (density =1000 kg/
) through a constant area-duct using a pitot tube and water-tube manometer. The differential head of water (density =1000 kg/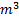 ) in the two columns of the manometer is 10 mm. Take acceleration due to gravity as 9.8 m/
) in the two columns of the manometer is 10 mm. Take acceleration due to gravity as 9.8 m/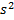 . The velocity of air in m/s is
. The velocity of air in m/s is
(A) 6.4
(B) 9.0
(C) 12.8
(D) 25.6
GATE-ME-2011
Hint 5.
Given Data
Density of air, 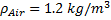
Density of water, 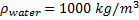
Acceleration due to gravity (g)=9.8 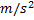 s
s
Manometer reading, 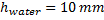
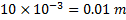
Velocity of air=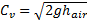
Where 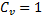
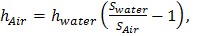
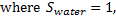
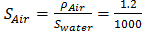
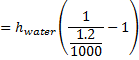
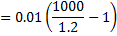
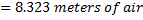
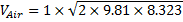
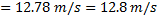
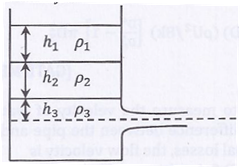
Question 6. A large tank with a nozzle attached contains three immiscible, inviscid as shown. Assuming that the changes in  are negligible, the instantaneous discharge velocity is
are negligible, the instantaneous discharge velocity is
(A) ![]()
(B) 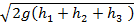
(C) 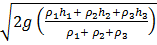
(D) ![]()
GATE-ME-2011
Hint 6. (Ans A)
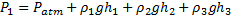
Bernoulli’s equation between (1) and (2)
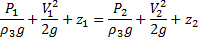
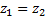 (Formeting)
(Formeting)
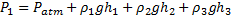
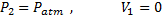
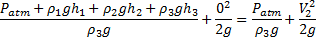
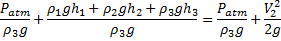
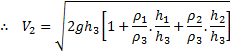
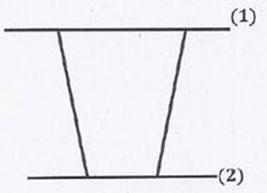
Question 7. Water is coming out from the tap and falls vertically downwards. At the tap opening, the stream diameter is 20 mm with uniform velocity of 2m/s. Acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/ . Assume steady, inviscidflow , constant atmospheric pressure everywhere and neglecting curvature and surface tension effects, the diameter in mm of the stream 0.5 m below the tap is approximately
. Assume steady, inviscidflow , constant atmospheric pressure everywhere and neglecting curvature and surface tension effects, the diameter in mm of the stream 0.5 m below the tap is approximately
(A) 10
(B) 15
(C) 20
(D) 25
GATE-ME-2013
Hint 7. (Ans B)
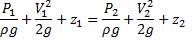
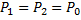
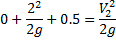
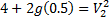
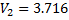
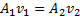
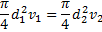
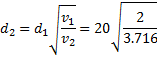
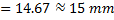
Answer keys
1. (D), 2 (D), 3. (B), 4. (C), 5. (C), 6. (A), 7. (B)