INTRODUCTION of CAMS and Types of CAM and Followers
A cam is a mechanical device used to transmit motion to a follower by direct contact. The driver is called the cam and the driven member is called the follower. In a cam follower pair, the cam normally rotates while the follower may translate or oscillate. A familiar example is the camshaft of an automobile engine, where the cams drive the push rods (the followers) to open and close the valves in synchronization with the motion of the pistons.
Types of cams
Cams can be classified based on their physical shape.
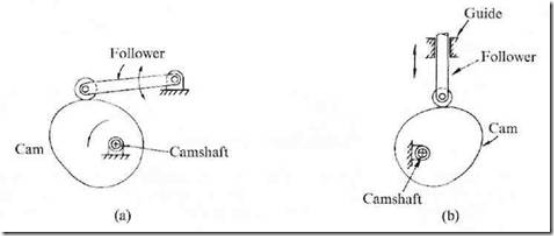
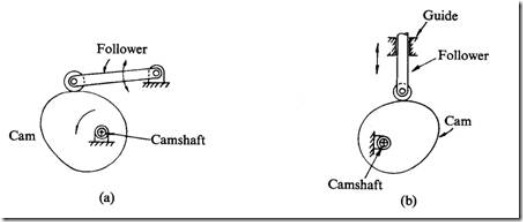
a) Disk or plate cam (Fig. 1a and b): The disk (or plate) cam has an irregular contour to impart a specific motion to the follower. The follower moves in a plane perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the camshaft and is held in contact with the cam by springs or gravity.
Fig. 1 Plate or disk cam.
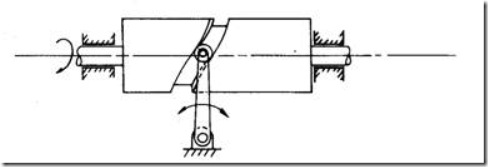
b) Cylindrical cam (Fig. 2): The cylindrical cam has a groove cut along its cylindrical surface. The roller follows the groove, and the follower moves in a plane parallel to the axis of rotation of the cylinder.
Fig. 2 Cylindrical cam.
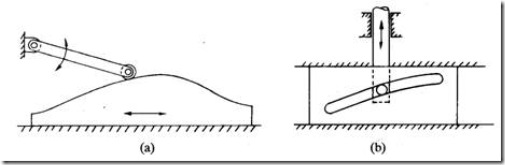
c) Translating cam (Fig. 3a and b). The translating cam is a contoured or grooved plate sliding on a guiding surface(s). The follower may oscillate (Fig. 6.3a) or reciprocate (Fig. 6.3b). The contour or the shape of the groove is determined by the specified motion of the follower.
Fig. 3 Translating cam
Types of followers:
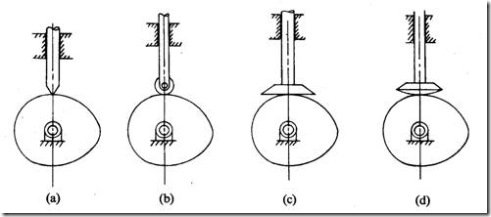
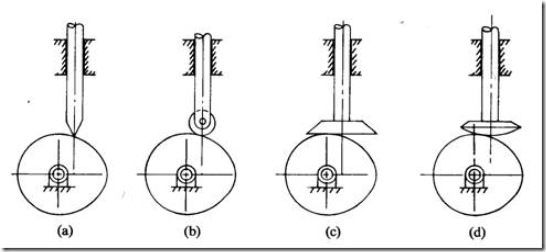
(i) Based on surface in contact. (Fig. 4)
(a) Knife edge follower
(b) Roller follower
(c) Flat faced follower
(d) Spherical follower
Fig. 4 Types of followers
(ii) Based on type of motion: (Fig. 5)
(a) Oscillating follower
(b) Translating follower
Fig. 5: Oscillating follower & Translating follower
(iii) Based on line of motion:
(a) Radial follower: The lines of movement of in-line cam followers pass through the centers of the camshafts (Fig. 4 a, b, c, and d).
(b) Off-set follower: For this type, the lines of movement are offset from the centers of the camshafts (Fig. 6 a, b, c, and d).
Fig.6 Off set followers
13 Responses to “INTRODUCTION of CAMS and Types of CAM and Followers”
Akshay Patil
Is there a case possible where cam is driven & the follower is the driver?
satheeshkumar.c
I like mech
vikash kumar
I like your cam follower discription
pavan ajay
how to download as pdf ?
ClintonKumah
This was very helpful
ORINYA CHUKWUDI GODWIN
This is very intelligible.
vipin
very helpful article
Andargir
I like it very well
admin
Thanks
Mani Ratnam
press ctrl+p to print the page as pdf…
Shanthanu
It is simply easy to understand. It is very useful.
zoritoler imol
Keep working ,remarkable job!
nwokora miracle Moses
this site is very helpful