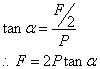Intermittent motion mechanisms
An intermittent-motion mechanism is a linkage which converts continuous motion into intermittent motion. These mechanisms are commonly used for indexing in machine tools.
Geneva wheel mechanism
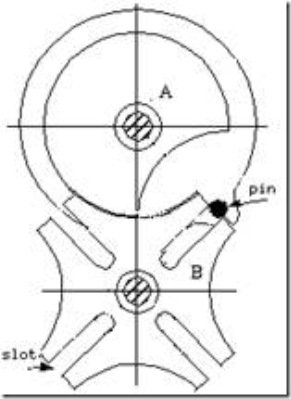
Fig.1: Geneva wheel mechanism
In the mechanism shown (Fig.1), link A is driver and it contains a pin which engages with the slots in the driven link B. The slots are positioned in such a manner, that the pin enters and leaves them tangentially avoiding impact loading during transmission of motion. In the mechanism shown, the driven member makes one-fourth of a revolution for each revolution of the driver. The locking plate, which is mounted on the driver, prevents the driven member from rotating except during the indexing period.
Ratchet and pawl mechanism
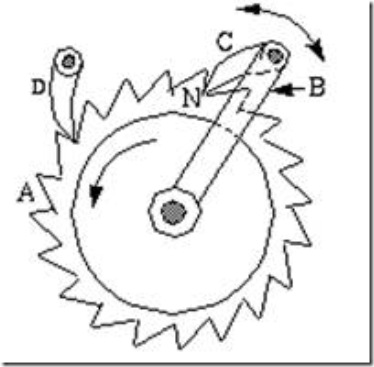
Fig.2: Ratchet and pawl mechanism
Ratchets are used to transform motion of rotation or translation into intermittent rotation or translation. In the fig.2, A is the ratchet wheel and C is the pawl. As lever B is made to oscillate, the ratchet wheel will rotate anticlockwise with an intermittent motion. A holding pawl D is provided to prevent the reverse motion of ratchet wheel.
Other mechanisms
Toggle mechanism
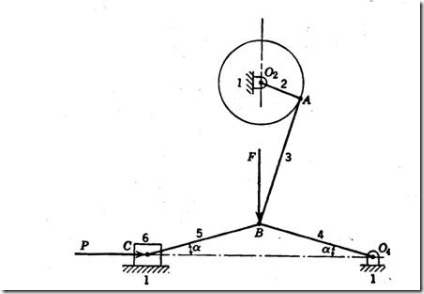
Fig.3: Toggle mechanism
Toggle mechanisms are used, where large resistances are to be overcome through short distances. Here, effort applied will be small but acts over large distance. In the mechanism shown in fig.3, 2 is the input link, to which, power is supplied and 6 is the output link, which has to overcome external resistance. Links 4 and 5 are of equal length.
Considering the equilibrium condition of slider 6,
For small angles of α, F (effort) is much smaller than P(resistance).
This mechanism is used in rock crushers, presses, riveting machines etc.
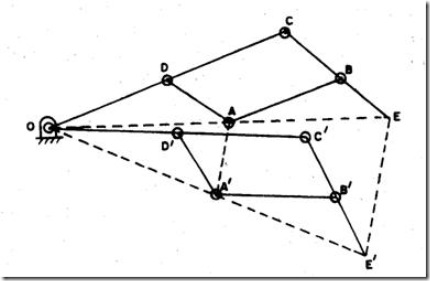
Pantograph
Pantographs are used for reducing or enlarging drawings and maps. They are also used for guiding cutting tools or torches to fabricate complicated shapes.
Fig.4: Pantograph
In the mechanism shown in fig.4 path traced by point A will be magnified by point E to scale, as discussed below.
In the mechanism shown, AB = CD; AD =BC and OAE lie on a straight line.
When point A moves to![]() , E moves to
, E moves to![]() and
and ![]() also lies on a straight line.
also lies on a straight line.