To determine the COP and Tonnage capacity of a Mechanical Heat pump.
Apparatus Used: – Compressor, Condenser, Evaporator, Capillary Tube, Ammeter, and Voltmeter.
Theory: –
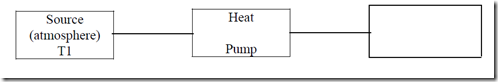
A mechanical heat pump is mechanical equipment which is used to supply the heat to the system, where it is installed, and maintain its temperature more than that of surrounding. Mechanical heat pump absorbs heat from surrounding (atmosphere). Work input to a heat pump is supplied by compressor. With reference to the fig. Heat Q2 is supplied to the room and temperature T2 is maintained above the T1 whereas heat Q1 is absorbed by the surrounding. Hence performance of heat pump is given by
C O P = Q / W
Where Q = heat removed from the system.
W = work supplied in compressor.
Theory: –
Coefficient of performance of mechanical heat pump is the ratio of heat removed by it and work supplied i.e.
C O P = Q / W
Where,
Q = heat removed
W = m. CpΔT watts.
m = mass of water in heating (condensation) or cooling (evaporator) tank.
Cp = Specific heat of water kJ / kg. K
ΔT = Initial and final temperature of water for unit time K.
W = Power consumer by compressor of unit time W.
= energy meter reading.
Technical Specification: –
Compressor = hermetically sealed of 1/3 T
Discharge pressure gauge = 0-3 – PSI
Suction pressure gauge = – 30-0-150 PSI
T1 & T2 are temperature of discharge suction side 0°C
T3 and T7 are temperature of water 0°C
T2, T3, T5 and T6 are temperature of inlet and outlet of heating and cooling coil.
Procedure: –
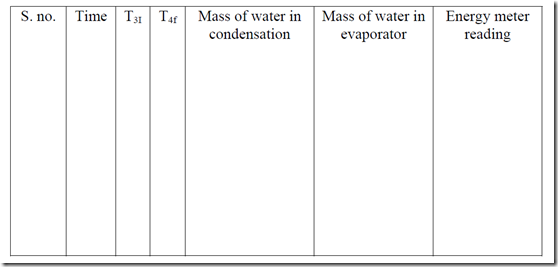
Fill measured quantity of water in condenser and evaporator banks and note down the initial temperature of tanks by means of selector switch as T4i. Now note down the energy meter and switch on the power supply to compressor. Run the compressor for unit time (say 30 minute) and note down the change in temperature of T4f and energy meter reading. Above procedure may be repeated for cooling coil also.
Temperature sensor details: –
1. T1 = Temperature Sensor: Fixed at Compressor Discharge Line
2. T2 = Temperature Sensor: Fixed after Condenser
3. T3 = Temperature Sensor: Inside hot water tank
4. T4 = Temperature Sensor: fixed after capillary tube
5. T5 = Temperature Sensor : Inside cold water tank
6. T6 = Temperature Sensor : Fixed at Compressor Suction Line
Observation Table
Calculation:
Q = m.Cp T =……………. Watts
W=……… Watts
COP = Q/W…………… %.
Precautions: –
1. Use stabilized power supply.
2. Drain the water from tanks after performing experiment.
3. When apparatus is no longer in use condense the refrigerant.
4. Use stop watch for time measurement.
Result: –
Viva Questions: –
1. Explain the working principle of mechanical heat pump?
2. What is the COP of mechanical heat pump?
3. What is the difference between air conditioning and mechanical heat pump?
4. How the cooling and heating is done in mechanical heat pump?
One Response to “Lab Manual | To determine the COP and Tonnage capacity of a Mechanical Heat pump”
vikram singh
very good manual
can you provide notes of RAC ???????